Cannabis production is a tough game, but those that can take the heat can reap huge payoffs. Knowing how to maneuver through the regulations, innovations, research, and trends can leave growers and processors scrambling to keep up in this fast-paced environment.
As a relatively young and immature industry, large scale marijuana cultivation, processing, and other supply chain services are throttled by federal restrictions and consumer misperceptions about the safety of certain concentrate extraction processes and cannabis in general.
Despite the high tax rates and licensing costs, interstate commerce limitations, and a bevy of other burdensome business challenges, pot businesses have essentially struck gold. Global cannabis sales are experiencing incredible year-over-year growth with no sign of slowing down.
As the cannabis production market continues to be fueled by consumer demand, cannabis cultivation and processing needs will need to keep up with its popularity as is evidenced by the stunning expansion across the world with the U.S. standing as its leading model for success.
Cannabis Production by State
Cannabis oil fuels the United States’ derivative product segment’s wide and diverse product categories including concentrates, tinctures, edibles, and topicals. Cannabis extracts offer consumers a range of products with different delivery methods to meet different lifestyle and wellness needs.
Licensed cannabis processors transform the raw hemp and cannabis plants into a money-making oil that can become the base for vape cartridges, beverages, transdermal patches, and other innovative products, to name a few.
Plant processing companies in the United States have grown at a quicker rate than even the already fast-growing cannabis industry. Marijuana is, by far, the fastest-growing industry in the country and the market is being increasingly supported by cannabis extract revenue.
A 2019 BDSA report elaborated on the processing market’s unlimited potential. Concentrates represented merely 10 percent of the United States market in 2014. Cannabis concentrates have rapidly shot up to account for 27 percent of the market in 2019 due to innovations in extraction technology.
In BDSA’s forecast model, the concentrate market will grow to “nearly match flower sales” with sales estimated in the $8-billion range by 2022. If federal legalization happens in the near future, the market’s sales prospects could skyrocket.
Vaping, in particular, is driving concentrate sales since it’s perceived as a healthier and discreet choice among consumers. As investors bet big on extraction, they’re soon realizing the unique challenges and the untapped potential of scaling their cannabis cultivation and processing capabilities.
California
California is undeniably the leading cannabis market in terms of sales and job growth in the United States. It’s no wonder you’ll find plenty of extraction success stories here. One survey found that California users’ preferred delivery method was vaping cannabis oil over smoking dry herb.
In the Golden State, concentrates have even started to outsell traditional flower buds. According to BDS Analytics, concentrates represented 37 percent of the sales compared to 33 percent from flower in 2018. This was the first time concentrates began showing their true potential in California.
A shining example of the rise of the extraction industry in California has been Northern California’s Procan Labs. After starting out of a garage (like marijuana companies do) in Oakland as a trimming service, Procan saw a gap in the market for cannabis processing and sought out to build the best extraction facility. Today, it handles marijuana from the state’s top growers.
In October 2019, the company announced it moved into a new 23,000 square foot processing and manufacturing facility to keep up with the state’s insatiable demand for concentrates. Procan’s over $8 million investment allows it to “produce double the output of most of [their] competitors.”
Colorado
Colorado’s market size is almost just as large as California’s and keeps on getting bigger. In this mature marijuana market, extraction companies are vying to become the most trusted processor in the game. Mile High Labs is one of these leading suppliers in Colorado and beyond, to say the least.
Mile High wasn’t always the biggest hemp processor in the world. Founded in 2016, the company has added hundreds of jobs to the local economy. Its expansion of labs into Loveland, Boulder, Cope, and Broomfield over the years has significantly grown its cannabis production capacity.
In October 2018, Mile High Labs announced a $35 million Series A financing from institutional and private equity investors. This was the largest Series A financing in marijuana history. It was a considerable achievement in an industry plagued by banking and lending limitations. GMP certification is the cherry on top that make it a trusted supplier for the international CBD market.
Washington
In Washington, concentrates represent about 40 percent of the state’s legal sales. In 2011, Xtracted Laboratories opened the state’s first large scale lab for processing weed. After outgrowing their original Georgetown location, Xtracted moved into its Seattle facility in 2012 with great governmental support.
Its Seattle facility received approval from city and state officials as well as the fire marshall, a level of cooperation unheard of at the time. With its expansion in Portland, Maine and Talkeetna, Alaska, the company has staked a strong claim in these rural and up-coming markets.
Oregon
Oregon’s oversupply of pot has affected farmers, but the state’s extract market has been relatively unscathed. In fact, the state’s extract sales increased to 31 percent in 2018 from half that number in 2014, while flower sales dropped from 67 to 44 percent between the same time period.
Founded in 2016, Halo Labs started off in Oregon and grew to command over 20 percent of the state’s market. In October 2018, it expanded into Las Vegas, Nevada with an 8,000 square foot facility and launched three house brands and one private label showing the limitless possibilities open in cannabis production.
In November 2018, it tapped into the Southern California market with a 1,600 square foot facility with a capacity of 120,000 grams of distillate per week. In 2019, they went international after completing a strategic partnership with Bophelo Bioscience in Lesotho in Southern Africa, effectively bringing their expertise to the African continent.
Cannabis Biomass and Live Resin
Cannabis and hemp biomass is the lifeblood of the green economy. Originally, the plant’s biomass referred to only the plant stalk and leftover bud after processing, but has now come to refer to any part of the harvested cannabis female plant including its trichome-covered buds. Of course, there are those who still frown upon this modern and all-encompassing use of the term.
A dynamic interplay between cannabis plant growers, brokers, and processors work together to grow, sell, and process thousands of pounds of biomass per month for THC and CBD-rich extracts. Of course, biomass can have varying levels of quality from low-grade hemp for mass market consumption to small-batch cannabis from a female plant with niche appeal.
Each batch of biomass features potency levels ranging from five to 25 percent cannabinoids and terpenes by weight. Some plant growers will send a representative sample of its plants to a third party lab for chemical and potency analysis. Carefully auditing the growers’ plant material is essential to producing the best extract from the plants.
Most hemp biomass growers use their plant material for industrial purposes including the production of biofuel, building materials, paper, clothing, and other consumer goods. Some cannabis producers select the most premium female plants to extract marijuana oils, distillate, isolate, and other concentrate products at scale.
CBD Isolate
One one end of the consumer spectrum is the wellness segment who avoids the psychoactivity of THC in favor of its more subdued isolate products. High-quality plant biomass undergoes a solvent-based extraction process to isolate only the CBD compound and a refining process to remove the residual solvent.
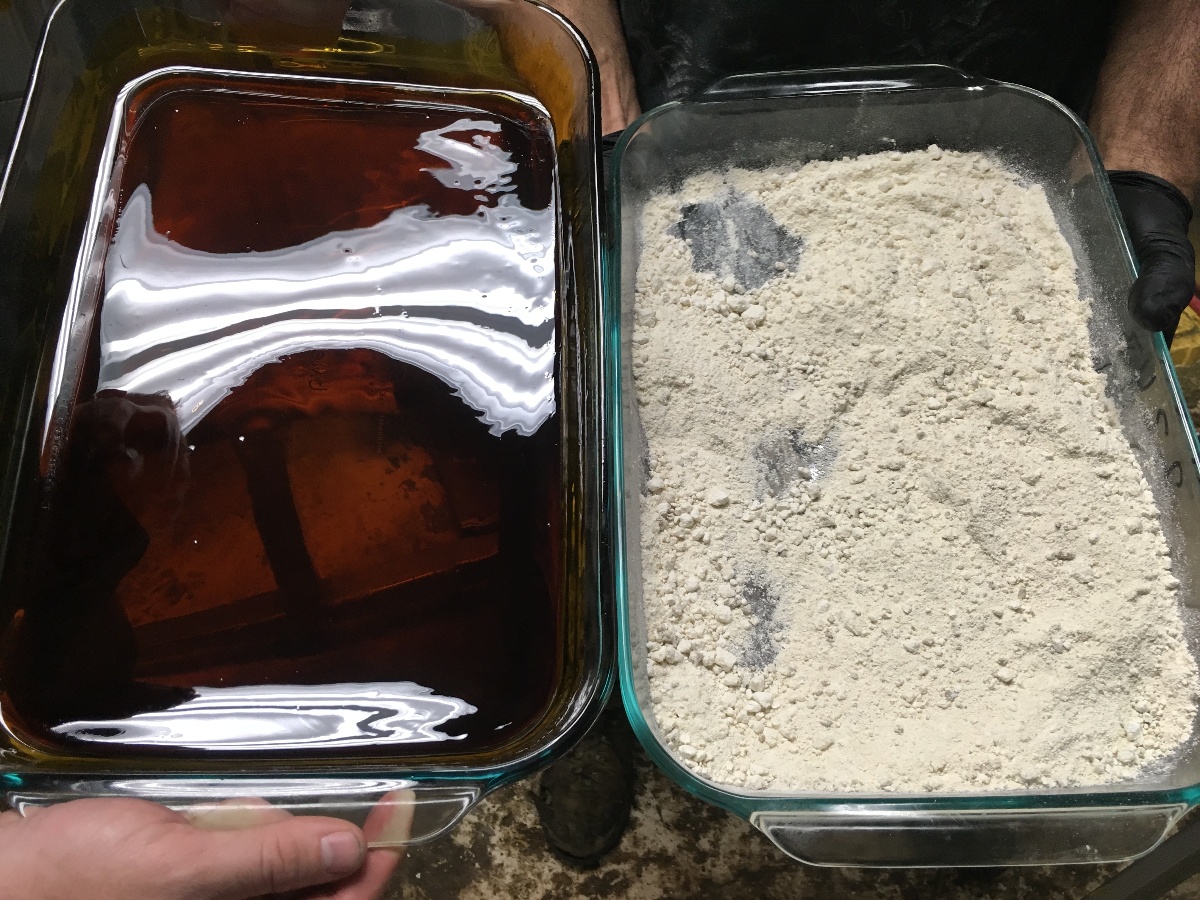

CBD isolate contains up to 99.9 percent CBD and comes in a crystalline form that can be ground-up into a powder for easy dosing. CBD isolate does not contain any other cannabinoids, terpenes, or flavonoids, although some cannabis producers add a touch of terpenes for flavor.
Live Resin
Unlike isolate cannabis products, live resin marijuana and hemp production seeks to retain as much of the plant’s original cannabinoids, terpenes, flavonoids, and other therapeutic oils. Traditional biomass undergoes a drying and curing process, which allows the chlorophyll and moisture to evaporate, but also removes terpenes.
Live resin, however, uses buds frozen right after growers harvest their female plants to capture their water weight and active compounds. Hydrocarbon (butane and propane) solvents are the preferred choice among extractors due to its ability to separate the most amount of compounds without losing out on as many terpenes.
After the frozen plant material is packed into a vessel, the chilled solvent washes over the plant material to keep temperatures down and terpene levels up. After the initial separation process, the resin is placed in a vacuum chamber at low temperature to evaporate its residual hydrocarbons and other undesirable compounds.
As producers aim to preserve the plant’s individual compounds, you get into the territory of full-spectrum cannabis products. Full-spectrum captures the complete chemical profile of the plant. High-terpene full-spectrum extracts (HTFSE) take it a step even further and preserve the highest terpene levels on the market. They’re the pinnacle for extract connoisseurs featuring an enchanting smell compared to the odorless isolate.
In a world where the marijuana consumer is plagued and satiated by variety in extract products, it’s essential for marijuana production companies to grow a business that is capable of creating a wide range of marijuana extract products for value and premium consumers.
Cannabis Licensing Challenges
Submitting a marijuana license application can leave entrepreneurs on the edge of their seat waiting for a response. Some applicants hire out an experienced application writer or consultant to advise them on the best way to build out their facility. They help companies avoid the dreaded denial, which can be challenged, but without assurances.
Local Laws
Municipalities can often ban cannabis production leaving operators to search for prime locations within weed-friendly cities among cannabis production deserts. Understanding the local regulations is the first step toward finding a place to do business. Processors must consider the local zoning laws to ensure a facility is up to code. Laws may essentially relegate companies to indoor cannabis cultivation.
Capital
Obtaining financial backing for any marijuana business is hard to do when banks fear federal repercussions for working with the cannabis industry. Financing is needed for application fees (often non-refundable), construction or renovation, personnel, equipment, and other overhead costs. Building an extraction lab, for instance, can cost between $400,000 and up to $800,000.
New Facility or Retrofit
Building a new facility can help operators design every aspect of the facility for maximum throughput. This, however, is a time and cost-consuming venture that can prove fruitless if the application is denied. Producers should consider the company’s growth objectives and how much capacity they need for years to come.
Retrofitting an active facility reduces the amount of time and money processors spend on building the facility. It can be tough to find the building that can accommodate the necessary systems determined by state and local regulations for the cultivation and processing of marijuana.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
Becoming GMP-compliant puts a company on the map toward national or global expansion. GMP requirements maximize quality throughout the marijuana production process. Because of a lack of national standards for extraction labs, the extraction industry is left without guidelines for processing marijuana and hemp.
Adhering to GMP regulations requires producers to choose GMP compliant equipment and design a lab with its rules in mind. Hiring an experienced team of engineers and suppliers is crucial to creating a safe, clean, and compliant extraction lab.
The licensing process is littered with plenty more challenges that can cause a license denial. Preparing for inspection and completing the application can take a toll on even the most season entrepreneur. Hiring experienced marijuana consulting services to take on the heavy lifting can save producers time and money in the long run.
How to Increase Cannabis Oil Production
If marijuana oil production accounts for a majority of marijuana products being sold, it stands to reason that extraction companies would want to grow their extraction yields to keep up with demand. Of course, sourcing the highest-possible quality plants is critical to delivering a premium product. Beyond getting high-quality raw plant material, the right extraction system can grow a company’s throughput.
.jpg?width=1200&name=Untitled%20design%20(23).jpg)
Closed-loop marijuana equipment has been built to handle ethanol, CO2, and hydrocarbon solvents, each with their own advantages and disadvantages. Hydrocarbon extraction, however, stands out among the rest for its innate ability to extract the finest quality oil in the fastest amount of time from cannabis plants. Butane and propane’s low boiling points allow it to preserve the aromatic terpenes from plants instead of losing them in the extraction process.
While yield alone isn’t the sole indicator of marijuana oil production efficiency, it’s a critical factor to consider. Above all, a product’s cannabinoid and terpene content determine its efficiency and profitability. Producers have to develop a product that consumers come to trust for its consistency, smell, and effects. Starting off with a quality source plant material allows extractors to get the most out of their cannabis plants.
High-tech butane hash oil (BHO) equipment can eliminate the need for additional purification steps such as winterization, which can delay the extraction process. The newest BHO systems can remove the undesirable elements such as fats, waxes, and pigments from the plants without damaging the cannabinoids and terpenes that can be lost during the refining stage.
A blend of propane and butane has shown to have the best results in extracting a fuller terpene profile from plants compared to butane alone. About 30 percent of butane and 70 percent butane can yield insanely high levels of terpenes. As research mounts on the synergistic interaction between cannabinoids and terpenes, a larger consumer segment will be turning to full-spectrum extracts.
Part of increasing oil production involves producing the most refined plant material available to overcome the stigma of solvent-based and BHO products. Color remediation cartridge (CRC) technology is upending the fear of hydrocarbon products. CRC uses various media to filter dark colors, chlorophyll, lipids, toxins and more out of marijuana plants.
Oil filtration companies like Media Bros are providing modern extracts with the color and clarity they deserve. Their CRX filtration media works flawlessly for hydrocarbon extractions. Its high-surface area, non-swelling, large format media is meant to filter without slowing down the process. While some media require prior prep work, the CRX is heat-treated, dried, and ready for filtration.
The best way to grow oil production capabilities is to ensure every part of the supply chain is running like a well oiled machine from cultivation to retail. For vertically-integrated companies, controlling the cannabis cultivation aspect can help them maintain consistency across markets with varying regulations. Small-batch producers can compete by working with the best growers and providing a product with a more handcrafted feel.
Scaling Cannabis Production Challenges
Setting up the right systems can quickly prove insufficient with the rising demand for concentrates. From extraction efficiency to equipment costs and a host of other factors that affect the market, scaling can seem near impossible for the common production company. Luckily, the challenges to scaling marijuana production are not impossible to overcome.
Plant Material
As with any marijuana derivative, sourcing high-quality plant material from the right suppliers can put processors in a better place to succeed. Ideally, a processor wants to have their provider’s plant matter tested to ensure its purity and quality. Securing multi-year contracts could give companies stability to grow. It’s also important to purchase plant material from a group of suppliers to avoid depending on a single supplier in case of an emergency.
Staffing
Hiring the right team from the start can reduce any road bumps along the way, especially when it comes to the safety of the team and the lab. With marijuana extraction, producers can’t risk hiring someone without the right background, degree, and experience working with botanicals in a lab. While some automated solutions don’t require as much labor, technicians must still know how to safely operate the equipment while remaining compliant with state and local regulations.
Legal and Regulatory Obstacles
Apart from the hurdles of trying to be one of the lucky few to obtain a processing license, legal and regulatory obstacles hinder extraction companies’ ability to scale. Cannabis’ federal status as a controlled substance puts weed businesses at high risk for a variety of business issues. Without the right help, owners can succumb to the mounting pressure.
Laws can limit where marijuana can be produced and even what products can be made. Some markets have license caps leaving some producers without a license until the regulatory agency decides to dole out new permits.
Smart leadership encourages marijuana extraction facilities to be built with the FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practice operations. Adhering to these federal standards ensures facilities are operating in clean and controlled rooms. Running a business with local, state, and federal guidelines ensure the company is ready for legalization.
Banking
Due to federal restrictions, banking and lending from traditional institutions is essentially inaccessible for marijuana companies. As a result, companies face an uphill battle by solely operating in cash, which brings up even more issues related to tax compliance, accounting, transportation, and storage.
A hindered ability to raise capital creates the perfect recipe for consolidation from large scale companies. Companies with deep pockets have much greater flexibility in adapting to the varying set of laws across markets. Small-batch processors are left to survive by creating an artisanal product compared to the mass-produced extract.
Weed companies can’t write off traditional business deductions due to IRS tax code 280E, which prevents companies who engage in illegal activities from writing off certain business expenses. Without the proper investment channels, obtaining the funding to scale can take longer if it even happens at all.
Misperceptions
While extracts’ popularity are at an all-time high, a significant portion of consumers want extracts produced without solvents. In light of the recent vaping crisis, consumer sentiment is leaning toward a healthier and solvent-free alternative.
The great vape scare has also led lawmakers to ban flavored vape products from the market until they figure out more effective safety regulations. As flavored products become old news, producing naturally-flavored extracts will help skirt potential bans on additives.
Boost Cannabis Capacity
Overcoming the market and regulatory obstacles along with equipment and personnel limitations can leave a clear lane toward dominating the extract market. Boosting marijuana capacity at a manageable rate requires adapting to market trends and refining the extraction process.
Automation
Automated extraction is one way to improve a company’s ability to reduce costs and improve yields. Automated equipment reduces the need for extra extraction technicians needed to continually monitor the system. Instead, automated closed-loop extraction equipment streamlines the process without the need for extra labor.
.jpg?width=1200&name=Untitled%20design%20(24).jpg)
Consistency across product lines is crucial to maintaining positive relationships with suppliers and meeting customers’ exacting needs. Pre-programmed recipes in automated extraction systems allow processors to hone in a certain set of parameters for different types of starting plant material.
Diversification
There is no marijuana expansion without diversifying service offerings. Companies shouldn’t underinvest on equipment that is capable of transforming marijuana into everything from CBD isolates to HTFSE. Hydrocarbons, above all other solvents, are able to gently interact with the cannabis plant material without ruining any part of the liquid gold.
Small-Batch Processing
In a market full of consolidation and massive campuses devoted to research, cannabis cultivation, and extraction, there’s still room for the little guy. In this case, the small-batch plant producers hold a special place in the hearts and minds of connoisseurs and novice users alike. Boosting marijuana capacity at the expense of quality is never a good idea.
As one segment of consumers flocks to the cheaper vapes, oils, and edibles, others will gravitate toward the artisan-crafted ethos of small-batch cultivation companies. Having the right systems on hand to handle trichome-rich plants can help producers maintain superior quality and consistency over the long haul and cement their place in the highly competitive market.
Cannabis extracts are here to stay. Companies looking to get in on the ground floor of a burgeoning concentrate and cultivation market should be looking years ahead. Extracts may have started off as a niche cannabis industry, but recent technological innovation puts it on the fast track for producing innovative plant-derived products for medical and adult-use markets.