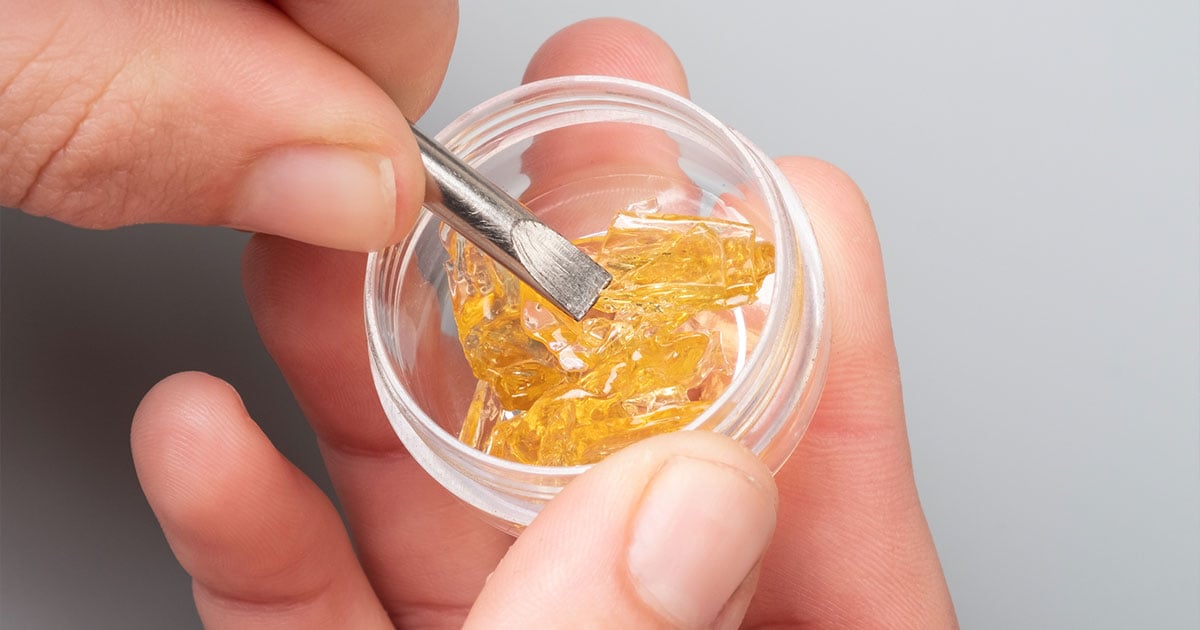
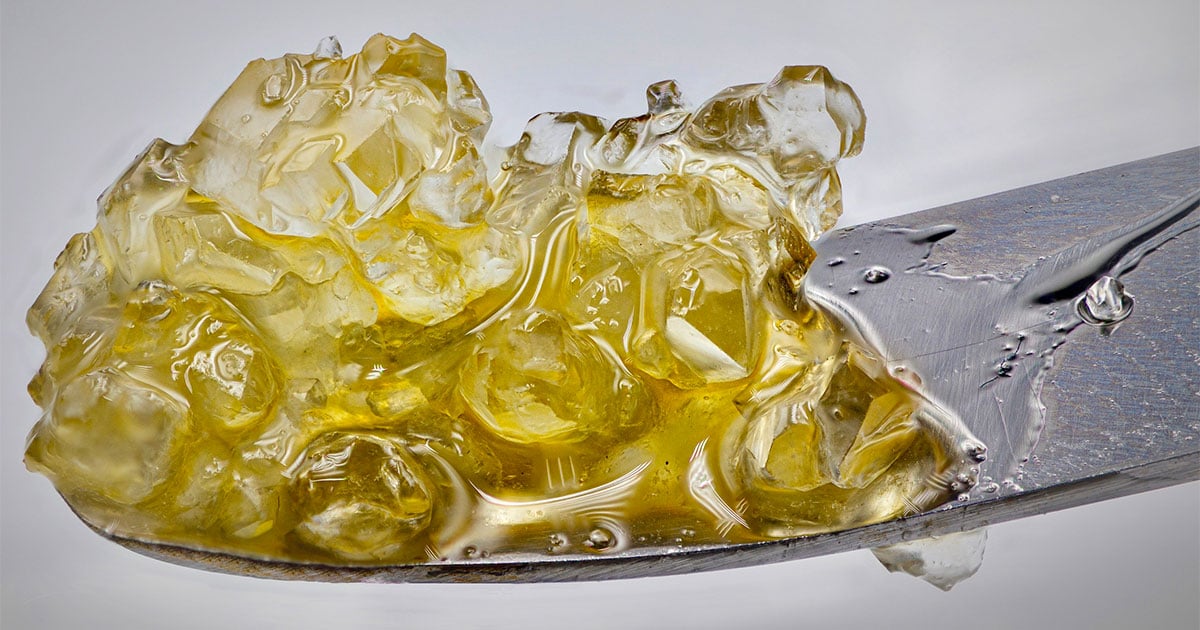
Modern cannabis extraction methods can produce high-quality cannabis extract and derivative products for medical and recreational markets. Although both cannabis markets use the same plant for extractions, each program is regulated differently.
In extractions for the medical (and recreational) market, processors use solventless or solvent-based extraction processes to create various cannabis products. Let’s take a closer look at how cannabis plants transform into extracts, edibles, or topicals sold at medical dispensaries.
Which Cannabis Components Are Targeted in Extraction?
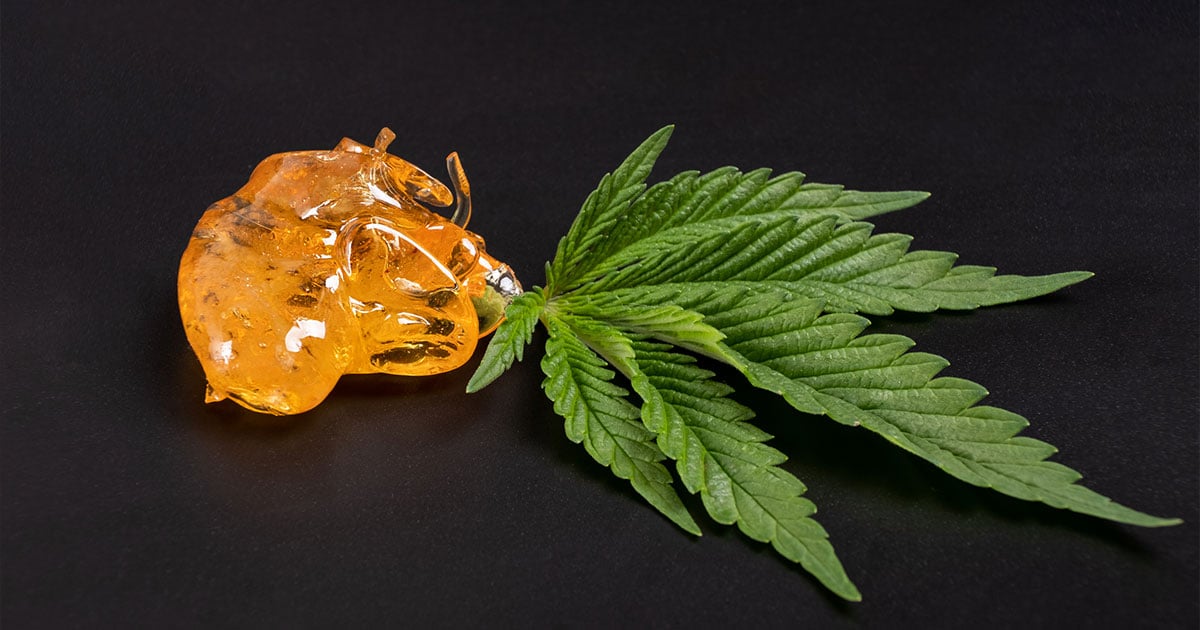

All cannabis extraction methods use the Cannabis sativa plant, although some processors may use hemp, a variety of cannabis that must legally contain less than 0.3% THC by dry weight, according to the 2018 Farm Bill.
Hemp is rich in cannabidiol (CBD), while cannabis has higher delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) concentrations. Cannabis flower often contains less than 1% CBD but can contain more balanced ratios of CBD-to-THC concentrations. Hemp (Cannabis sativa) is the same species of plant as cannabis. Unlike cannabis, hemp contains low levels of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), less than 0.3%.
Processors typically focus on extracting THC and CBD, the plant’s two main cannabinoids, while maintaining flavor profiles like terpenoids and other secondary properties such as ketones, ethers, esters, and flavonoids.
What are cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are natural cannabis compounds that resemble the body's naturally produced endocannabinoids such as anandamide and 2-AG. Cannabinoids are thought to correct endocannabinoid deficiencies, which can affect various biological responses.
The cannabis plant contains over 100 different cannabinoids. Cannabinoids and other beneficial compounds are stored in the plant’s trichomes, the bulbous resin glands mainly found on the buds and the stems and leaves in lower amounts.
Cannabis plants are ready for harvest when most of the plant’s trichomes have fully matured and turned an amber color.
Minor cannabinoids such as cannabinol (CBN), cannabichromene (CBC), and cannabigerol (CBG), to name a few, are found in trace concentrations, although growers are now beginning to breed strains to contain higher levels of these underrated compounds.
What are terpenes?
Terpenes, the plant’s aromatic compounds, can do more than give the strain its unique aroma. Preliminary research suggests that these heat-sensitive compounds can be essential in elevating health benefits and minimizing the adverse effects of cannabinoids.
Cannabis contains over 400 different terpenes. Although terpenes only make a fraction of the total compounds, they contribute heavily to the aroma and medicinal benefits. There are seemingly endless combinations of terpenes in different strains.
Cannabis processors and consumers are only recently focusing on the importance of terpene extraction to reap the full medical benefits.
Each terpene is believed to have different effects and scents. Common terpenes include:
- Myrcene
- Linalool
- Beta-caryophyllene
- Alpha-pinene
- Terpinolene
- Limonene
- Humulene
- Eucalyptol
- Camphene
What are other components found in cannabis?
Cannabis contains other beneficial components, including flavonoids, minerals, vitamins, ethers, esters, and ketones.
What is the difference between broad-spectrum, full-spectrum, and isolates?
Hemp extractions, in particular, can produce full-spectrum products, containing the plant’s complete spectrum of components, including THC. Broad-spectrum contains most components except THC, so it does not produce intoxication. CBD isolates contain up to 99.9% CBD.
Factors Affecting the Extraction Efficiency of Medical Cannabis
Several factors affect the extraction efficiency of the desired components from the cannabis plant material. Understanding the factors that affect the medicinal cannabis extraction process can help processors set up optimal conditions for extraction.
Here are some factors that affect the extraction efficiency of medical cannabis:
- Solvents
- Plant material
- Extraction technique
- Extraction run time
- Pressure
- Temperature
- Material-to-solvent ratio
- Agitation
- Solvent pH
Medical Cannabis Extraction Processes
In the cannabis industry, extraction processes can produce a wide range of extract types and infused products, including edibles, tinctures, vape cartridges, and topicals. Each product type has a different duration and onset of effects.
Choosing the right extraction method is critical to producing the desired product. For example, edibles may require the use of odorless and tasteless distillate in the recipe instead of a terpene-rich extract.
In the medical and recreational cannabis market, processors use two main extraction processes: solventless and solvent-based extractions.
- Solvent-based methods of extraction use chemical solvents (butane, carbon dioxide, or ethanol) in a closed-loop extractor to dissolve the plant’s trichome oils from the plant material, recycle the solvent, and purge the residual solvent. Different post-processing techniques can be used to create different extract types and filter certain compounds.
- Solventless extraction methods do not use chemical solvents. Instead, they use mechanical processes to break off or squeeze the trichomes from dried plant material. Solventless methods may be suitable for those concerned about extraction solvents.
Here are the most common cannabis extraction methods:
Butane Extraction
Butane hash oil (BHO) extraction is one of the most popular and efficient ways to extract all of the plant’s compounds, rather than just the most popular ones (i.e., CBD and THC). BHO extraction is better able to produce full-spectrum extracts and high-terpene full-spectrum extracts.
Light hydrocarbons (like butane and propane) have lower boiling points than other solvents, allowing processors to operate at lower temperatures and preserve more volatile terpenes. A butane/propane blend (70/30) is typically used to extract more of the terpenes than using butane alone.
Butane is a flammable and explosive solvent, requiring the proper safety measures (ventilation, gas detection, etc.) to keep extraction technicians safe. Otherwise, butane extraction processes are generally safe.
Since hydrocarbons are better able to extract terpenes, the butane and propane extraction process can produce the widest range of cannabis extracts, including live resin, terp sauce, distillate, and isolate.
Ethanol Extraction
Ethanol extraction uses high-grade alcohol to extract cannabinoids and terpenes from cannabis. Ethanol extraction is popular for its high throughput but can take out excessive chlorophyll, requiring post-processing to remove this bitter-tasting compound. The ethanol extraction process can be performed in cold and warm conditions.
Because ethanol has a higher boiling point than butane or propane, extractions can yield lower terpene levels. Generally, ethanol extraction is used to make distillates and isolates, not full-spectrum products with relatively high terpene levels.
Carbon Dioxide Extraction
Carbon dioxide (CO2) extraction uses supercritical CO2, a state of CO2 that has properties of a liquid and gas that can diffuse through the biomass like a gas and dissolve the resin like a liquid.
Subcritical CO2 extraction processes use lower operating temperatures and pressures than supercritical extractions. These parameters are used to extract the plant’s most sensitive compounds like terpenes. This method may take a longer time than supercritical extractions.
Dry Sifting
Dry sifting cannabis involves using a series of mesh screens to filter out trichomes of various sizes. Dried plant material is placed over the mesh screens and agitated to break off the plant’s trichomes.
Dry sifting produces kief that can be used alone to enhance the potency of dried herb or be compressed into various hash forms (ball, slab, etc.) and even be turned into rosin, which we will get into below.
This process can be performed at home with a multiple-chamber grinder. As you grind your cannabis, the bud falls into the middle chamber, and any loose trichomes fall through a screen into the bottom chamber. This product is known as kief.
Ice Water Extraction
Ice water extraction, also known as bubble hash extraction, uses fresh-frozen cannabis and has a similar extraction process to dry sifting, except this process occurs in a bucket full of ice water and lined with mesh screen bags.
As you gently stir the cannabis plant material in the ice-cold water, the trichomes break off, fall to the bottom of the bags through the filter, and can be collected to make full melt hash or live rosin. Fresh-frozen cannabis can better preserve the plant’s compounds at their peak ripeness.
Rosin Pressing
Rosin pressing is a solventless extraction method that uses heated plates to make rosin, a sticky and viscous type of solventless extract. A rosin press uses heat and pressure to compress the plant material and squeeze the cannabis resin.
Rosin can be consumed via a dab rig or e-rig or be used to make other products, including edibles, topicals, and tinctures. Live rosin undergoes a similar process to rosin, except it uses bubble hash as a starting material.
Create Better Medical Cannabis Products with Luna Technologies
Cannabis processors can elevate their hydrocarbon and ethanol extractions with Luna Technologies’ fully-automated cannabis extractors. Cutting-edge extraction technology keeps workers safe and pushes the boundaries of what medical cannabis products can be.