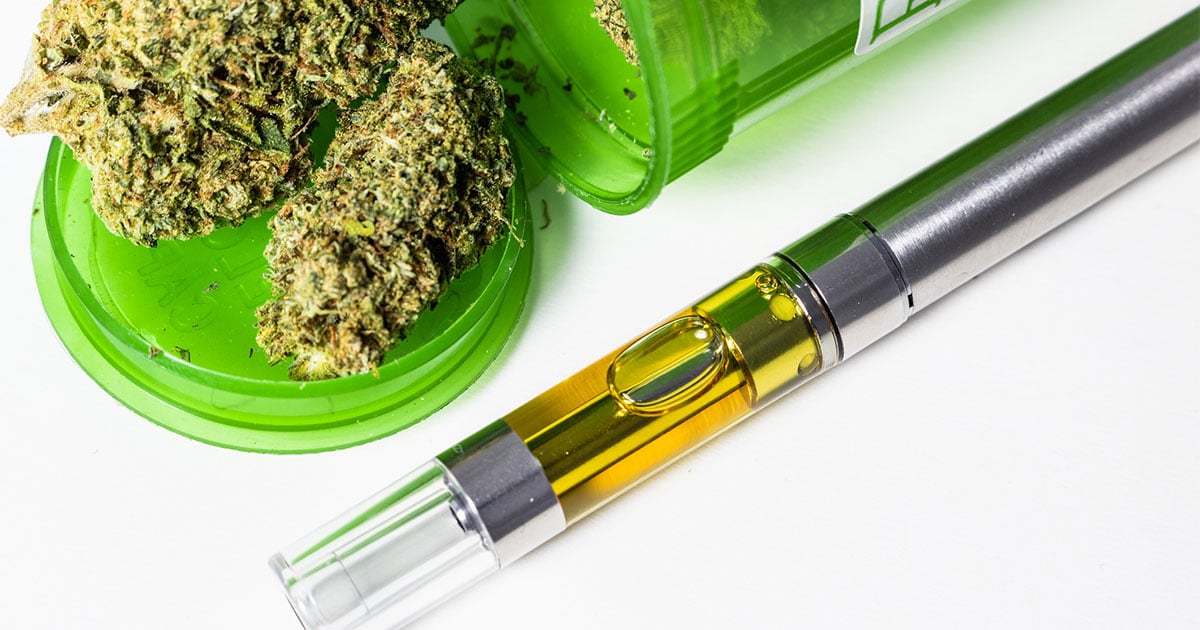
Dried and cured resin is the primary oil used for a variety of extracts, including vape cartridges. While many are buzzing about its live resin variety, cured resin can boast a high potency and full spectrum vaping experience, too.
Our cured resin vape cartridge guide will cover cured resin in detail, its production process, and the different types of oils available in vape cartridges. We will also describe the differences between cured and live resin to help you decide which one is best for you (Hint: Both of them are good!).
But first, a note on why distillate, the once popular method of extraction, is quickly fading into irrelevance in the cartridge market.
Is Distillate (and CO2) Dead in the Cartridge Market?
In today's competitive market, distillate and CO2 vape cartridges are quickly falling out of favor, because distillate and CO2 extraction processes can destroy many of the naturally occurring terpenes during production.
In order to mimic the strain’s terpene profile, processors may use synthetic terpenes to flavor the oil. They may also use cannabis-derived terpenes, which can result in extra labor and costs.
Ultimately, the process can be cumbersome and costly, resulting in a lower quality product over butane hash oil (BHO) extracts like cured and live resin carts.
As BHO extraction has improved, processors can now produce a high-terpene extract directly into a vape cartridge. Even a few years ago, BHO processes were not this efficient.
Now, inline refinement can remove the waxes and lipids while preserving the terpenes and cannabinoids, leaving behind a ready-to-vape product for cartridges. For businesses, this can mean massive operational savings and better quality products that consumers gravitate to.
Ultimately, CO2 and distillate-based products just are not worth it. Processors can lose up to 50 to 60% of their oil making distillate and destroying many of the naturally occurring terpenes. In addition, the process can take up to a week compared to the 24 hours needed to make BHO cartridges.
Cured and live resin are both high quality oils for use in vape cartridges. CO2 and distillate oils can create a decent product but it is just not BHO. While live resin is superior to cured resin, any resin made with light hydrocarbons tends to produce a more flavorful and aromatic product.
What Is Resin?

First off, let us discuss the resin nomenclature that has become popular in the industry over the past several years.
In cannabis labeling and marketing, resin refers to the sticky and microscopic trichome glands that form primarily on the cannabis plant buds and on its sugar leaves and stems in lower concentrations.
You may have also heard resin describe the black and brown tar residue that builds up in your cannabis pipe, bong, or dab rig, but, here, we will focus on its definition as a collection of cannabis trichomes as an oil.
Resin is the foundation of today’s wide range of consumer packaged goods, including edibles, topicals, tinctures, and extracts such as vape oils for pre-filled cartridges.
Understanding Trichomes
Inside these mushroom-like resin glands that make up concentrate-based products, a wide range of therapeutic compounds are formed and lost, depending on the stage of plant growth and production, strain genetics, and storage conditions.
Cannabinoids
Generally, resin contains a high concentration of the plant’s two main cannabinoids: cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). That is why you will mainly see CBD- and THC-rich vape cartridges.
While much of the research on cannabis has focused on THC and CBD, minor cannabinoids are also present in low amounts and may offer synergistic effects alongside THC and CBD.
Researchers have isolated over 100 different cannabinoids from the plant. Trichomes also contain minor cannabinoids such as:
- Cannabigerol (CBG)
- Cannabinol (CBN)
- Cannabichromene (CBC)
- Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV)
Terpenes
In addition to these minor cannabinoids, the trichome resin glands also contain the plant’s aromatic compounds, known as terpenes. Terpenes are found in trace amounts, and they may provide therapeutic benefits alongside cannabinoids.
Terpenes are found in many plants and herbs. Researchers have identified over 150 different terpenes in the cannabis plant. Each terpene has a unique aromatic note, contributing to a complex bouquet of aromas that vary by strain.
Common terpenes include:
- Myrcene
- Beta-caryophyllene
- Humulene
- Limonene
- Pinene
- Linalool
- Terpinolene
- Ocimene
- Eucalyptol
- Geraniol
In the wild, trichomes offer an evolutionary advantage since they can deter pests and animals and protect the plant from UV rays. For us, cannabis resin can be consumed to provide considerable relief from a wide range of conditions and symptoms.
In vape cartridges, the resin oil can be easily and stealthily inhaled as a vapor to produce nearly instant effects that can last for about two to three hours.
What Is Cured Resin?

Cured resin refers to a cannabis extract made from raw cannabis plant material that has been dried and cured before extraction. It is taking over the cannabis extract market, predominantly because of its profitability for the extractor; cured resin produces a higher yield with each run, requires cheaper biomass, and requires fewer steps to process. Extractors can also start with strain-specific dried cannabis whose terpenes will remain intact in the final product.
Almost every cannabis extract undergoes a drying and curing process and can be considered a cured resin product in the extraction sector. During the drying and curing process, the cannabis flower buds can lose most of their weight from the moisture loss.
Cured resin can come in a variety of extract forms including glass-like shatter, creamy budder, sticky wax, syrupy terp sauce, and vape oil for cartridges.
Now, let us get into specifics about the drying and curing process.
After plants are harvested, they are stored in a dark, climate-controlled room with temperatures ranging between 65 to 75º F and a relative humidity (RH) between 55 and 65%.
Creating a climate-controlled environment requires an HVAC system consisting of fans, an air conditioning unit, and a dehumidifier.
Drying
Drying can take between a couple of days to a couple of weeks, depending on the moisture level of the plant material and the storage environment. Drying temperatures are between 65º and 75º F and an RH between 0 and 55%.
One of the most effective ways of determining when the cannabis buds have been properly dried is when the branches audibly snap instead of bending.
After they have properly dried, they are manicured to remove the extra foliage, leaving behind only resinous buds with a high bag appeal. These ready-for-sale nugs are stored in an airtight container, usually a mason jar, sometimes oven bags, or plastic or ceramic containers.
Fresh Frozen
In contrast, fresh frozen cannabis completely skips the drying and curing stage. Instead, the flowers are immediately frozen when harvested to preserve their freshness and terpenes. The drying process, while necessary for the production of whole-flower products, can lose out on 30 to 40 percent of the strain's original terpene concentration through evaporation.
Curing
Curing the cannabis buds produces a better potency, flavor, and smell from the bud after the initial drying stage in the production of cured resin. If the process is rushed or not completed properly, the cannabis smoke can be harsh and its aroma may not be as refined.
Airtight containers are stored in a cool, dry, and dark space. Curing can take anywhere from about 30 days for the quickest cure but can go on for much longer, resulting in a more refined smoke. 90 days is recommended for a solid cure.
Curing temperatures range between 65º and 75º F and RH between 55 and 65%. During the curing process, the airtight containers are opened for several minutes at a time every day in a process known as “burping.”
Burping refers to the moisture exchange that occurs when the buds are sealed in an airtight container and opened to allow the moisture to dissipate and expose the buds to fresh air.
Mason jars are opened a few times a day for about 15 to 20 minutes to allow the moisture to exchange for the fresh air.
Overall, the curing process is integral to the quality of the final product. By the end of the process, the dried and cured cannabis can be extracted using a variety of solventless and solvent-based techniques and turned into a cured resin for use in a variety of products.
What Is Live Resin?

Live resin is the latest extract form to make a name for itself in the cannabis extraction sector. Its cannabis bud preservation technique differs significantly from traditional drying and curing processes used for cannabis extracts. The result is a better tasting and smelling product.
Instead of undergoing the long and laborious process of drying and curing flower buds, live resin is created by harvesting the plants and immediately freezing them to subcritical temperatures. Essentially, the freezing preserves the plant’s volatile compounds at their peak maturity.
During the drying and curing process, the harvested cannabis plants’ moisture levels and chlorophyll are removed. However, the trichomes also begin to degrade, especially in the presence of heat, light, and oxygen.
While the drying and curing process produces a much smoother smoke, it can destroy many of the plant’s temperature-sensitive terpenes, the compounds responsible for the plant’s unique aroma and flavor, not to mention the possibly elevated health benefits.
Freezing the plant preserves its sensitive cannabinoids and terpenes. As a result, cannabis oil that is produced from fresh-frozen starting material has a deeper and more complex aroma, although it can produce a darker, more golden-colored extract.
Live resin’s consistency can range between a sauce and wax. Its consistency varies depending on the strain and the extraction techniques used.
Today, live resin products and vape cartridges can fetch a premium price for their connoisseur-grade quality. The future of cannabis seems to be in terpene-rich extracts, especially high-terpene full-spectrum extracts (HTFSE).
Cannabis Vape Cartridges: What Is In Your Oil?

In terms of cannabis extracts, vape cartridges offer convenience, portability, and functionality all rolled into one. Vape cartridges allow you to enjoy your cannabis oil on the go wherever you go without the harsh and smelly smoke of flower.
Also known as vape carts, these pre-filled cannabis oil cartridges can simply screw into a 510 threaded battery and be ready for use. Some vape cartridges come in proprietary forms and only work with compatible devices such as Pax Era pods and the Pax Era.
It is important to remember that not all cannabis vape cartridges are created equal. Low-quality cartridges are made of plastic, while high-quality ones are made of glass, ceramic, and metal. They can also contain lower quality oil.
Vape cartridges are generally pre-filled with between half a gram or 1 full gram of cannabis oil. Cannabis oil can vary in its concentrations of cannabinoids and terpenes. Some carts include artificial flavors, thinning agents, botanically-derived terpenes, or cannabis-derived terpenes.
Generally, vape carts have a high concentration of THC although some have higher concentrations of CBD or more balanced ratios of THC and CBD.
Apart from the hardware and cartridge material, the oil is one of the most important aspects of the cartridge. Determining what is in the oil can help you decide which vape cartridge is right for you.
Cured and Live Resin Vape Cartridges
In order for the vape cartridges to work properly, the cannabis oil must have the right viscosity to effectively vaporize inside the device. Here is where there are differences between the type of cannabis oil used in vape cartridges.
Cured resin vape cartridges are usually made from CO2 or hydrocarbon extraction. Each has its pros and cons. CO2 cartridges use the CO2 extraction process and are able to retain many of the cannabinoids and some terpenes, although at a high upfront cost for equipment. Hydrocarbon extraction is able to better preserve these terpenes and improve overall quality.
Live resin vape cartridges are usually only made with hydrocarbon extraction due to the solvent’s innate ability to reap more of the plant’s terpenes and cannabinoids. In live resin cartridges, consumers are able to consume a higher concentration of terpenes compared to standard cured cartridges.
Cannabis distillate cartridges, a type of cured resin, provide users with refined cannabis oil containing almost a majority of cannabinoids. Distillates are usually produced using ethanol or CO2 solvent. During the distillate-making process, the oil can lose out on its undesirables and also its terpenes.
Cannabis distillate, or even CO2-extracted vape carts, can offer high potency and even some aromatic appeal but may lack the nuance of a full-spectrum cured and live resin cartridge made with light hydrocarbons.
Some manufacturers may infuse terpenes back into the distillate and CO2 extracts after purification with botanically derived sources to resemble the flavor of the cannabis strain. However, distillates and CO2 vape carts will not resemble the original chemical profile precisely.
In its highest form, cured resin vape cartridges made with light hydrocarbons can be made from a near full spectrum of cannabinoids and terpenes, even if the terpenes must be separated and re-introduced. The result is a strain-specific product that tastes and smells just like the original strain.