Fire safety professionals developed new building and life safety codes to keep up with the ever-changing cannabis industry. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) added Chapter 38, "Marijuana Growing, Processing, or Extraction Facilities," to the 2018 Edition of NFPA 1 Fire Code to address common marijuana production hazards.
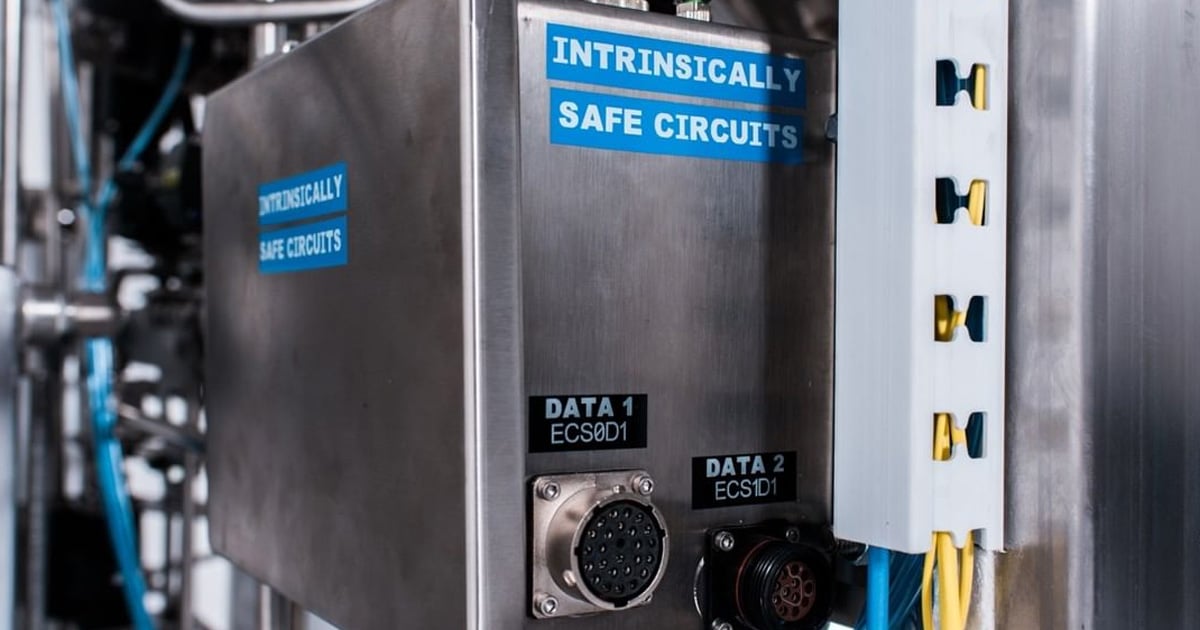

1. Extraction Equipment
Description
Equipment that isn’t listed for the specified use, must submit a technical report to the AHJ for review in accordance with Section 1.15 documenting the design and peer review of the equipment.
Explanation
Because Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratories (NRTL) such as UL and ETL haven’t caught up with the quickly evolving cannabis industry, nor written code for extraction equipment, the NFPA relies on non-NRTL third-party reviewers to approve all equipment.
2. Signage
Description
Extraction rooms shall have easily accessible safety data sheets (SDS). Additionally, the NFPA 704 hazard rating diamond sign and no smoking sign shall be displayed in front of the extraction room door. Any other hazard warning signs shall be posted where applicable.
Explanation
Employees and contractors should be aware of any workplace hazards associated with the materials with which they work. Safety data sheets are an excellent standardized way to pass along this information. The same goes for emergency responders when they arrive at a scene. NFPA hazard diamonds are a quick reference for emergency response so that they know what hazards they can expect and can prepare appropriately.
3. A Means of Egress
Description
Extraction rooms that handle hazardous materials shall provide at least one exit access door fulfilling the following:
- The door shall swing open in the direction of egress travel
- The door shall self-close or automatically close
- The door shall have panic or fire exit hardware
Explanation
During a safety event, personnel should be able to exit the building quickly and easily. Stopping to pull open a door can slow you down and expose you to hazards for longer. Doors that swing outward and panic hardware aid in quick egress.
4. Extraction Room
Description
Extraction processes besides CO2 and nonhazardous materials, the equipment shall be located in a room of noncombustible construction. The room shall strictly be used for extraction processes.
Explanation
Limiting exposure to hazardous areas is an engineering control to mitigate health and safety risk. By using the extraction room for only extraction processes, personnel are only exposed to the hazardous area when absolutely necessary. According to OSHA, this is the best technique for mitigating risk if a hazardous process is selected.
5. Gas Detection System
Description
Extractors shall use an approved continuous gas detection system. The system shall alert the extractor when the gas detection threshold is no greater than 25 percent of the gas LEL/LFL. Systems shall be provided with constant noninterlocked power.
Explanation
Most hazardous solvents used in cannabis extraction are odorless and colorless. Because personnel cannot see or smell the hazardous material, they may not be able to identify and assess a safety event. A continuous gas detection system acts as the operator's sixth sense to ensure they are aware of dangerous levels of hazardous vapor.
6. Change of Extraction Medium
Description
Where the medium of extraction or solvent is changed from approved material in the technical report, the report shall be revised at the owner’s cost and submitted for review prior to use.
Explanation
The analysis and conclusions of the "technical report" are derived from specific solvents and extraction media. When these change, the results of the technical report change, too, thereby necessitating a second review.
NFPA Chapter 38 has helped set a standard set of codes and regulations for marijuana extraction facilities by addressing prominent fire service concerns. The 2018 NFPA 1 Fire Code should be used as a guide for developing safe cannabis processing facilities. As the cannabis industry changes, nationwide standards will aim to protect marijuana extractors.